Rethinking remote work infrastructure and scaling product engineering is urgent. In times when coronavirus potentiated has accelerated digitalization around the world there is no choice at all. Every single industry has been impacted positively or negatively with social isolation. From events to entertainment and supply chains needed to became digital quickly. As we continue to move into the new normal, more innovative uses of edge computing and cloud computing will emerge.
Consequently, companies started to rethink remote infrastructure in order to guarantee better conditions of remote work for their employees. At last, offer an experience similar to that of the office is mandatory to keep the company competitive. So, in this context, it will be relevant to understand the pros and cons of Cloud Computing and Edge Computing. Keep reading to find more!
How/Why a distributed world enforces the need for remote work infrastructure and scaling product engineering teams
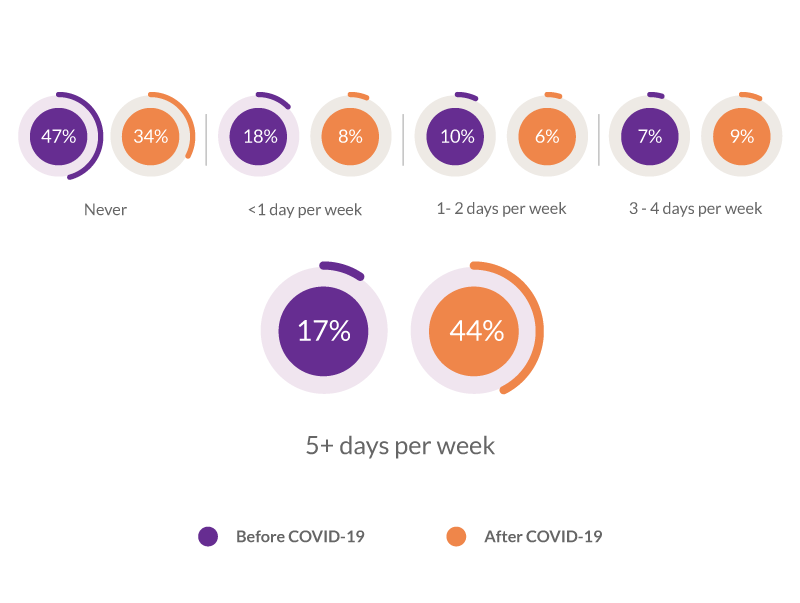
Before the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic remote work was an optional reality for most teams.
According to Statista, 17 percent of U.S. employees worked from home 5 days or more per week.
Now, this share increased to 44 percent because of the pandemic.
Remote work, also called telework or working from home (WFH), provided a solution, with employees performing their roles away from the office.
And this work only os possible if is supported by specialized technology and tools based on performance.
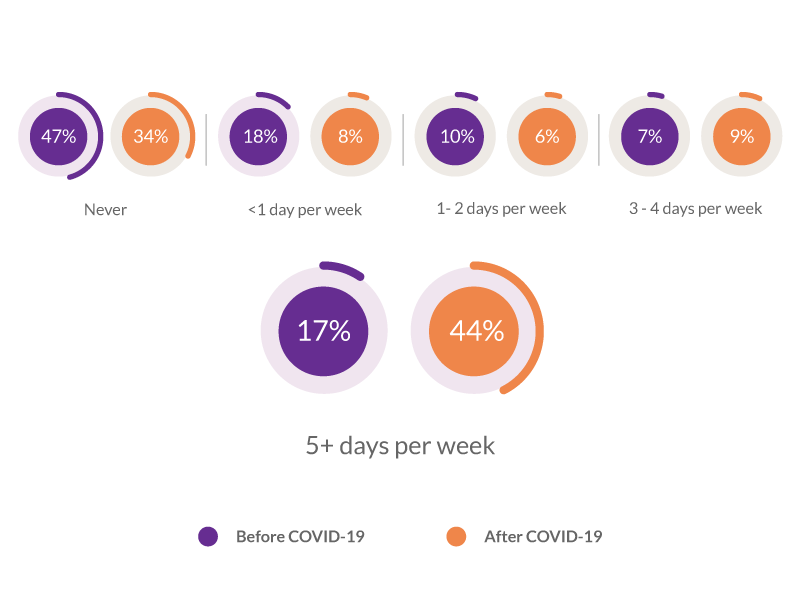
Source: Statista
At the same time, remote work fostered the growth of cloud and edge computing around the world.
According to research from the IBM Institute for Business Value (IBV):
- 84 percent of executives expect edge applications to positively impact operational responsiveness within the next five years
- The worldwide end-user spending on public cloud services is forecast to grow 18.4% in 2021 to a total $304.9 billion.
So, the pandemic and remote working scenarios have underlined the vitality of infrastructure for business continuity with remote workforces and seamless online collaboration.
First, it is slow, expensive, and wasteful to send a large amount of data without fast infrastructure for storage and processing.
Second, because of the increase of the acceleration of other technologies, such as IoT devices, even before the pandemic.
Cloud Computing and Edge Computing: meaning, basic concepts, and key differences
Basically, cloud and edge computing differ in the way these infrastructure stores and process databases, networking, and software. While Cloud computing uses remote serves or data centers for storing,
Nearly 85 percent of companies believe cloud adoption is necessary for innovation. At the same time, the Edge AI Software market is forecasted to reach 1.12 trillion dollars volume by 2023.
Cloud Computing’s basic concept
Cloud Computing is a technology model of distributed data processing in which some scalable information resources and capacities are provided as a service to multiple external customers through Internet technology.
For enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) Cloud Computing can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
3 Components of Cloud Technology: SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)?
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
Benefits of Cloud Computing
High infrastructure availability, self-service provisioning, elasticity, mobility, workload resilience, migration flexibility, broad network access, disaster recovery and pay-per-use.
Edge Computing basic concept
Edge Computing is a kind of infrastructure to store data away from centralized cloud computing.
In Edge Computing data is stored and used locally, on the device, e.g. a smart phone or IoT device. Edge computing delivers faster decision-making, local and offline data processing, as well as reduced data transfer to the cloud (e.g. filtered, computed, extra- or interpolated data), which saves both bandwidth and cloud storage costs.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Edge computing is an ideal technology to reduce the strain on data centers.
So, those functions that need cloud connection have adequate bandwidth, while those use cases that benefit from reduced latency and offline functionality are optimized on the edge.
So, Edge applications reduce the volumes of data that must be transferred, the traffic that results from the transfers, as well as the distance the data travels. That’s why Edge Computing is the key to the first real-world search engine.
Edge Computing and Cloud Computing Key Differences
Edge computing and cloud computing are both useful and relevant technologies. Both have different strengths and ideal use cases.
Together they can provide the best of both worlds:
- Decentralized local storage and processing
- Making efficient use of hardware on the edge and central storing and processing of some data
- Enabling additional centralized insights, data backups (redundancy), and remote access.
To combine the best of both worlds, relevant and useful data must be synchronized between the edge and cloud in a smart and efficient way.
Which is better for data security and privacy while scaling product engineering teams: Cloud or Edge computing?
By 2022, some three-quarters of enterprise data will be processed outside the cloud, so it’s safe to say that it’s more than just a passing trend.
How to keep the privacy and security of data is the main challenge while scaling product engineering teams in a remote infrastructure.
Edge Computing
Whether your data is stored locally or on the cloud, if hackers access your credentials, the risk of a breach is equal.
Additionally, edge computing expands the potential attack surface by having sensitive data stored and processed across a more extensive array of systems.
It gets much harder, even to the point of becoming a practical impossibility, to protect ubiquitous computing environments at scale, simply because the footprint grows too large.
A recent study by Tech Republic found that two-thirds of IT teams considered edge computing as more of a threat than an opportunity, mainly because of this dramatically increased endpoint attack surface.
On the other hand, if compromised, the data compromised is clearly defined, making the notification and subsequent actions manageable.
Cloud Computing
And there is the possibility of expanding security capabilities to all edge devices. This includes:
- Encryption of data both at rest and in transit
- Changing default passwords
- Maintaining control through a centralized management dashboard to control how devices interact with the computing environment.
Most businesses, however, have one major concern when it comes to cloud computing. The level of data protection depends mostly on the security state of each data center.
Businesses that want to protect their most sensitive data can purchase private cloud deployment models to manage on-site.
Others with a smaller budget can opt for hybrid cloud models which can be customized to meet their specific data protection needs.
How is latency in Cloud and Edge Computing? What suffers more lag failure?
Edge computing is used to process time-sensitive data, while cloud computing is used to process data that is not time-driven.
Besides latency, edge computing is preferred over cloud computing in remote locations, where there is limited or no connectivity to a centralized location.
In the cloud computing model, connectivity, data migration, bandwidth, and latency features are pretty expensive. This inefficiency is remedied by edge computing, which has a significantly less bandwidth requirement and less latency.
By applying edge computing, a valuable continuum from the device to the cloud is created, which can handle the massive amounts of data generated.
Costly bandwidth additions are no longer required as there is no need to transfer gigabytes of data to the cloud.
It also analyses sensitive IoT data within a private network, thereby protecting sensitive data. Enterprises now tend to prefer edge computing.
This is because of its optimizable operational performance, which addresses compliance and security protocols, alongside lower costs.
The bonus of reduced operational strain in scaling the product engineering team
All these emerging technologies ultimately have to be discussed, keeping in mind how and where these applications and software are hosted.
Starting from your business goals, and deciding on the right infrastructure — then apply the newest technologies.
Some analysts claim that edge computing will replace cloud computing because computing will become decentralized and the need for the centralized cloud will fade.
However, that will not be the case, as their functions are different. Edge computing devices are designed to gather and process data on-site quickly and analyze data in real-time.
It doesn’t focus on storing data. Cloud computing, on the other hand, is based on infrastructure and can be easily scaled according to needs.
Thus, edge computing is ideal for applications where every millisecond counts, while cloud computing works best for applications that are not time-sensitive. Instead of replacing cloud computing, it’s safe to say that edge computing will complement it.
Good technical decisions are made by great professionals. Ubiminds can help you find them.
Ubiminds combines the best of each world when it comes to growing your software business.
Ubiminds also supports tech companies in scaling software engineering teams.
Stop wasting time now and start focusing on product development, not hiring processes. Let Ubiminds spare you 75% of the work!

International Marketing Leader, specialized in tech. Proud to have built marketing and business generation structures for some of the fastest-growing SaaS companies on both sides of the Atlantic (UK, DACH, Iberia, LatAm, and NorthAm). Big fan of motherhood, world music, marketing, and backpacking. A little bit nerdy too!